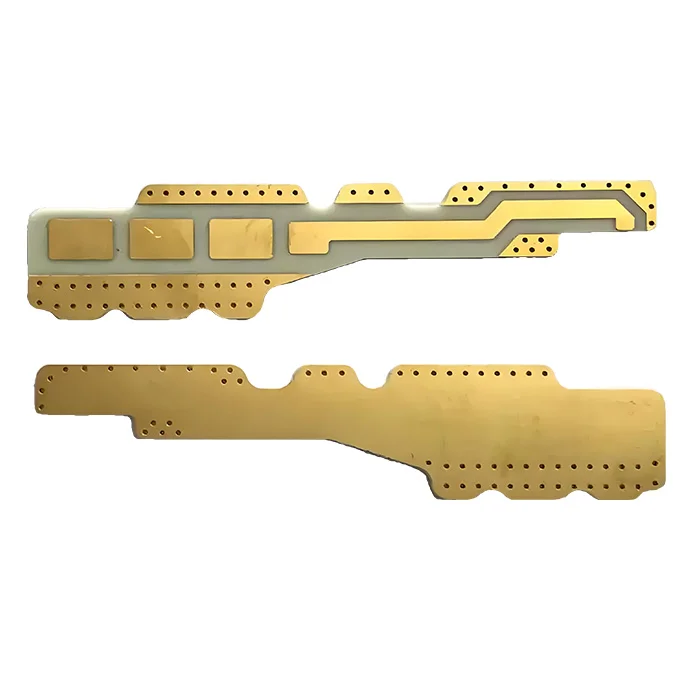
Heavy Copper RF Microwave PCB
$60.90
Heavy copper RF microwave PCB is a specialized PCB with thicker copper than standard high-frequency PCBs, typically ≥ 3 oz. Combining the properties of heavy copper with premium RF high-frequency performance, it provides robust power handling and precise signal integrity in high-power applications and environments with mechanical or thermal stress, such as 5G telecom, aerospace, and high-power RF and microwave systems.
Shipping fee and delivery date to be negotiated. Send inquiry for more details.
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Claim a refund if your order is missing or arrives with product issues, our support team would deal with your refund within 24 hours.
| Layer Counts | 4L |
| Base Material | Rogers |
| Board Thickness(mm) | 1.6mm |
| Max board size(mm) | 570*850mm |
| PCB size tolerance | ±0.2mm |
| Min. Hole Size | 0.15mm |
| Min. Line Width | 4mil |
| Copper Weight | 3oz |
| Surface Finish | ENIG |
| Certificate | UL, IPC-6012, RoHS, ISO 9001, ISO14001 |
 Heavy Copper RF Microwave PCB
Heavy Copper RF Microwave PCB
| 5 star | 0% | |
| 4 star | 0% | |
| 3 star | 0% | |
| 2 star | 0% | |
| 1 star | 0% |
Sorry, no reviews match your current selections
Questions & Answers
1. Does MOKOPCB support mass production?
Yes, we have the capacity to handle small to high-volume PCB production with automated assembly lines.
2. Where does MOKOPCB ship from and to?
We deliver our goods from our facilities in Shenzhen, China.
3. What’s the difference between the standard PCB and the heavy copper PCB?
The standard PCB usually uses 0.5–2 oz/ft² copper, while heavy copper PCB uses 3 oz/ft² to 20+ oz/ft² copper. Heavier copper means the PCB can handle higher current and dissipate heat faster than the standard one. However, heavy copper is pricer due to the copper cost and specialized fabrications.
4. How thick should PCB copper be for RF applications?
Different RF applications have different copper thicknesses. For low-power RF, 1–2 oz is enough to balance the cost and performance; for high-power RF, 3-6oz is suitable for improved heat dissipation and current capacity.
5. How does copper thickness affect RF performance?
Compared to thin copper, heavy copper reduces conductor loss and improves signal integrity. Thicker copper ensures sufficient conductive depth to handle higher currents without excessive heating, and reduces skin effect and impedance control.
6. Does heavy copper reduce thermal issues?
The heavy copper significantly mitigates thermal problems. Its lower resistance reduces heating, and high thermal conductivity dissipates heat effectively.
7. Why are laser-drilled microvias better for RF than mechanical drills?
Laser-drilled microvias are superior because the vias drilled by laser are more precise and smoother, and have consistent impedance and minimal parasitic effects. Additionally, lasers avoid rough surfaces and delamination risks, ensuring better signal integrity at RF and microwave frequencies.
8. Does the copper roughness affect signal integrity?
Yes, copper roughness increases conductor losses and phase distortion because of the skin effect. For RF and microwave high frequencies, smoother conductors like rolled copper are preferred to reduce impedance, improve signal integrity, and maintain consistent performance.