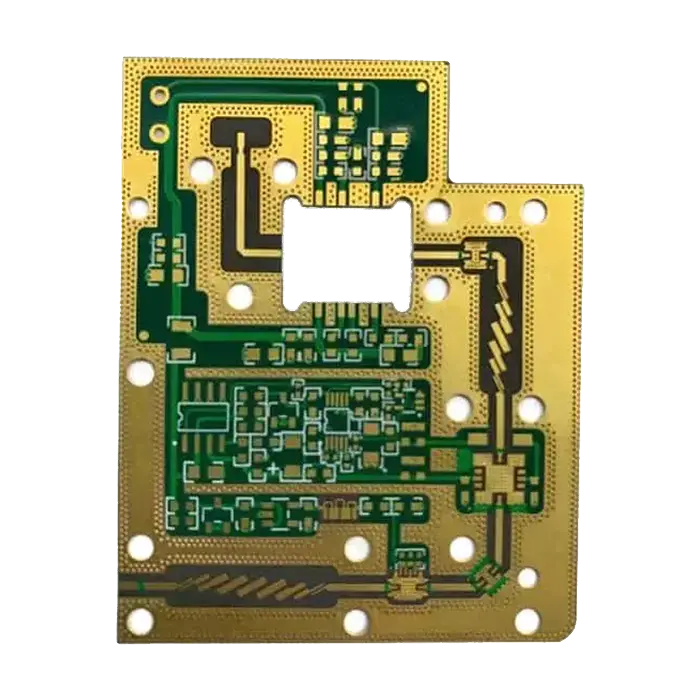
High Frequency Rogers 4350 Material PCB
$88.00
As its name suggests, this PCB is perfect for applications that require stable performance at high frequencies (up to 100 GHz). Made of a strengthened glass hydrocarbon/ceramic material, high frequency Rogers 4350 material PCB offers a low dielectric constant (3.48±0.05 at 10GHz). It is a reliable alternative to PTFE materials in high-frequency environments.
Shipping fee and delivery date to be negotiated. Send inquiry for more details.
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Claim a refund if your order is missing or arrives with product issues, our support team would deal with your refund within 24 hours.
| Layer Counts | 4L |
| Base Material | Rogers 4350 |
| Board Thickness(mm) | 1.0 |
| Max board size(mm) | 570*850 |
| PCB size tolerance | ±0.3mm |
| Min. Hole Size | 0.3mm |
| Min. Line Width | 4mil |
| Copper Weight | 1oz |
| Surface Finish | ENIG |
| Certificate | UL, RoHS, ISO, and REACH |
 High Frequency Rogers 4350 Material PCB
High Frequency Rogers 4350 Material PCB
| 5 star | 0% | |
| 4 star | 0% | |
| 3 star | 0% | |
| 2 star | 0% | |
| 1 star | 0% |
Sorry, no reviews match your current selections
Questions & Answers
1.What is the thermal conductivity of Rogers 4350B?
Rogers 4350B material has a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.69 W/m·K, offering excellent thermal management.
2.What is the dielectric constant (Dk) of Rogers 4350?
Rogers 4350’s dielectric constant is close to 3.48, delivering reliable electrical performance over a wide frequency range.
3.What materials are included in the RO4000 series?
The RO4000 series includes several high-frequency materials, including RO4350B, RO4003, RO4450, and RO4835.
4.Why Rogers 4350 material PCBs are more and more popular?
Rogers 4350 PCBs are gaining popularity due to several key advantages:
▪Low electrical signal loss
▪Low moisture absorption
▪Precise impedance control
▪Better thermal management
5.What are the two main dielectric properties that affect signal losses?
The two key dielectric properties that influence signal losses in PCBs are:
Dissipation factor (Df): This affects signal speed and impedance.
Dielectric constant (Dk): It indicates how much signal energy is lost.