V-Scoring
During the PCB manufacturing process, there are a variety of panelization methods used such as V-scoring, tab routing, and solid tabs. Among these methods, V-scoring is one of the most widely used techniques and provides a low cost and easy method to separate individual boards from a multi-board panel with high precision. This helps to streamline both the fabrication and assembly processes.
What Is V-Scoring in PCB?
V-scoring is a technology used to panelize a PCB board by creating angled grooves at the top and bottom of a board. It is also known as V-cutting or V-grooving, and it shapes V-shaped channels that serve as predetermined separation points between individual circuit boards. These grooves are much like the segmented design of a chocolate bar and they enable us to separate each board easily and cleanly from the panel.

How the V Scoring Process Works
The V scoring procedure involves two blades that are at arbitrary angles, i.e., 20, 30, 45 and 60 degrees. These blades act as wheels with numerous gears that are used as knives for making the score. One of the blades is at the top and the other at the bottom rotating point-point-point with a certain distance so that the PCB can pass through. This distance determines the remaining thickness between the two V-cuts. The rest of the thickness acts as a carrier for the subpanels or manufacturing panels that keep the PCB units together. After the PCB board assembly process, the subpanels are then cut into individual PCB assembly boards.
Benefits of V Scoring
V-scoring is a technique that poses several advantages and assists in optimizing the PCB production and assembly process:
- Cost-Effective Production: It enables more boards to be produced in a single panel and this helps to eliminate the wastage of materials, thus cutting down the cost of overall production.
- Increased Production Speed: By using this technique, the speed of separation of PCBs becomes faster and more accurate, and finally, the assembly process is quicker and the turnaround is shorter.
- Improved Panel Stability: V-Scoring enhances the stability of PCB boards and makes them very structurally sound, hence reducing the possibility of panel damage when handled and shipped.
- Flexible Design Integration: The use of V-scoring requires very few changes in the PCB layout and therefore provides more design and layout planning freedom.
Challenges of PCB V-Scoring
Though V-Scoring has a number of advantages, there are limitations as well:
- Fracture Risk: It is challenging to control how deep the scoring will be. Too shallow will fail to separate PCB, while too deep will ruin PCB structure.
- Limitations with Complex Designs: Boards with complex design layouts (high density of component placement) or those that are not rectangular-shaped might not lend themselves well to V-Scoring and instead might require other depaneling processes.
- Material Restrictions: V-Scoring would not be applicable on certain types of PCB such as thick PCB or rigid-flex PCB, and may need other processes.
PCB V Scoring Vs. Tab Routing
When deciding between PCB V-scoring vs Tab Routing, it’s important to understand their distinctions, the table below highlights the key differences:
| Factor | V-Scoring | Tab Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | High-volume, rectangular PCBs | Irregular shapes, prototypes |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Higher cost due to routing |
| Speed | Faster separation | Slower, requires tab removal |
| Edge Quality | Rougher edges | Smoother finish |
| Design Flexibility | Suitable for simple layouts | Accommodates complex design |
Choose V-scoring when:
- Manufacturing high volumes of identical, rectangular PCBs
- Cost efficiency is the primary concern
- Fast production turnaround is required
Choose tab routing when:
- PCBs have irregular shapes
- Edge quality is critical
- Components are positioned near board edges
Guidelines for Applying V Scoring in PCB Panelization
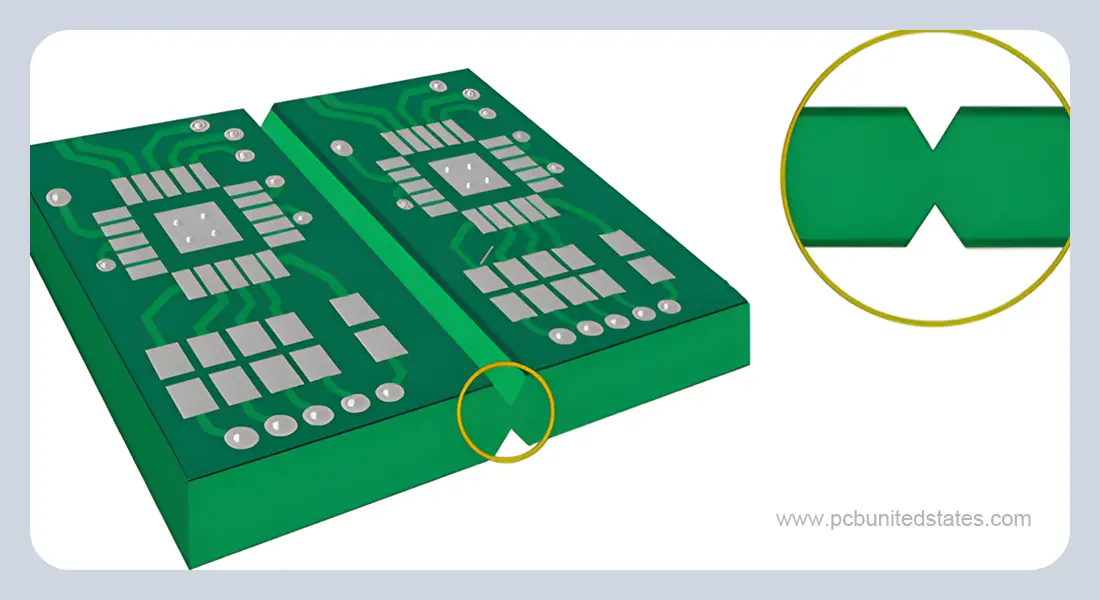
- Scoring lines must be straight and oriented either vertically or horizontally.
- Minimum PCB size: 60mm × 45mm; Maximum size: 600mm × 1200mm.
- Available scoring angles: 20°, 30°, 45°, and 60° (30° is commonly used).
- Scoring angle tolerance: ±5°.
- Blade alignment tolerance: ±0.05mm between upper and lower blades.
- Remaining material thickness tolerance: ±0.10mm.
- Recommended remaining thickness:
- For finished board thickness ≤1.0mm: 0.3mm.
- For thickness >1.0mm: Typically 1/3 of total thickness.
- Minimum remaining thickness: 0.25mm (+0.05/-0.00mm).
- Minimum spacing for skip scoring: 5mm.
- Minimum width of breakaway rails: 5mm.
- Recommended only for board thicknesses >0.6mm.
Design Considerations for V-Scoring
When implementing V-scoring as the part of your PCB panelization strategy, it is necessary to pay attention to several important issues:
Board Shape: V scoring works best on rectangular and square-shaped PCBs, so in the case of an irregular shape, there might be a more effective type of panelization technique than V-scoring
Component Placement: Due to V scoring, designers will have limited options regarding component placement along the edges of the PCB, especially when grooves are relatively close to critical components. In this case, the designer will need to avoid placing certain components and traces too close to the score lines
Groove Width and Depth: The groove size should be taken into consideration as regard to the PCBs thickness to avoid over-cutting or under-cutting, which can ultimately ruin the structural integrity of the circuit board.
Material Selection: The selection of suitable materials is important when designing PCB V scoring because inappropriate material selection may result in fracturing or delamination upon separation.
Minimum Slot Width: When designing V scoring in a PCB layout, it is important to consider the minimum width of slots that will determine how many PCBs can be contained in a single panel, ultimately affecting manufacturing efficiency.
Edge Clearance: Designers must provide sufficient clearance between the groove and the edge of the PCB to maintain structural integrity. The designer should ensure that there is enough clearance between the groove and the PCB edge to prevent breakage of the PCB.
Precision V-Scoring Services for Efficient PCB Panelization
Applying V-scoring techniques in the PCB manufacturing process can eliminate the need for routing space and thus maximize the panel utilization. Meanwhile, this technique saves on material resources, accelerates the manufacturing speed, and streamlines the fabrication and assembly processes.
At MOKOPCB, we are equipped with state-of-the-art equipment to implement V scoring with consistent groove depth, precise blade alignment, and optimal remaining thickness. In addition, we can also provide other PCB panelization solutions that fit a variety of circuit boards. From PCB design, fabrication to assembly, MOKOPCB can handle them under one roof. Need tailored services for your PCB projects? Contact our technical team today for a free consultation or to get a free quote!
Contact Us
Got any questions or inquiries? Fill out the form and we will get back to you soon

