Annular Rings
The annular rings form an important part of designing PCB, as they allow reliable electrical connection between different layers through vias. Their dimension and placement have a direct effect on the integrity of the connection and the performance of the overall board. Lack of proper design of the annular rings may result in signal loss, intermittency of connection, or even noise in sensitive electronic components. In this blog, we will explore what annular rings are, their importance, how to measure their sizes as well as some critical design tips to ensure a reliable PCB.
What Is a PCB Annular Ring ?
An annular ring is the ring-shaped copper pad on a printed circuit board that surrounds a drilled hole. The hole is used to place component leads or wires, and these rings make a solid electrical and mechanical connection when the component pins are inserted and soldered. Therefore, these rings should be manufactured and designed correctly to make electrical performance reliable and stable across the board.
How to Calculate Annular Ring Size
In the ideal case, the drilled hole should be centered within each annular ring to provide good electrical connection between the via and the PCB layers. The proper width of these rings can be calculated by using the following formula:
Annular ring size = (Pad diameter – Hole diameter) / 2
For example, when the copper pad diameter is 30 mils and the hole diameter is 14 mils, then the ring size would be: (30 – 14)/ 2 = 8 mils.
Why Annular Ring Size Matters?
When the PCB annular ring is too narrow, it likely will not provide adequate conductive surface to ensure a good mechanical and electric bond. This may cause poor or unstable connections, especially during soldering or thermal cycling. While if the ring is too wide, it can also create issues. Oversized annular ring would occupy more space of the board, which means that there is less space to contain other components.
Thus, it is essential to design an appropriate size of annular rings. As a rule, the minimum ring width should be 0.15 mm (6 mils), and the drilled sizes generally range from 0.2 mm to 6.3 mm.
What Are Teardrops?
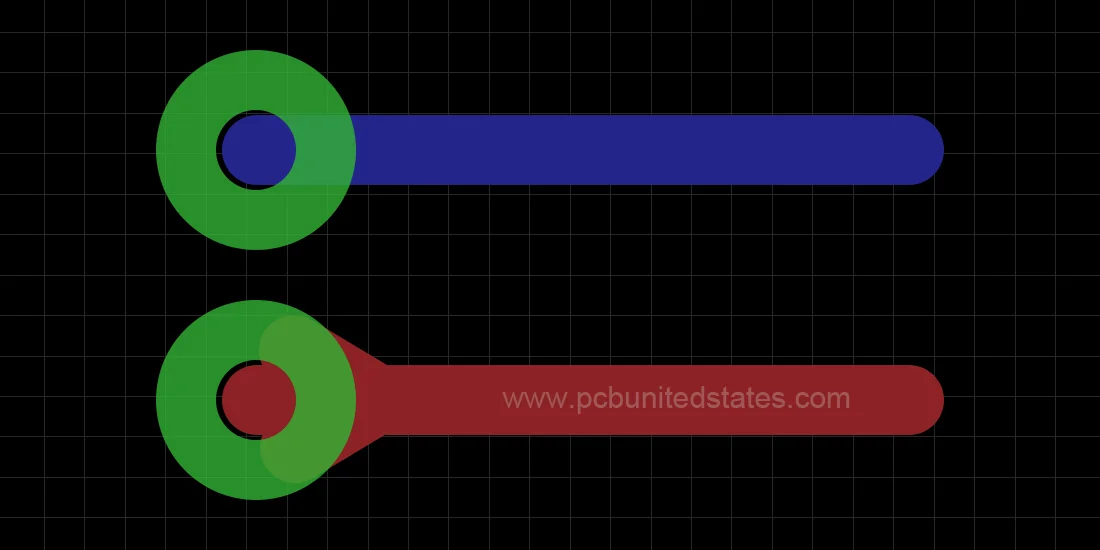
The term “teardrop” owns its name due to its droplet-like shape, as you can see in this figure below. A teardrop pad refers to add extra copper at the position where an annular ring and a PCB trace intersect, so as to strengthen the connection point. This added material assists in improving structural strength, particularly, under mechanical or thermal stress.
During the drilling process, there may be some drill misalignment that can potentially remove too much copper from the junction point between the via pad and trace. As a result, weak or broken electrical connections may occur. During manufacturing, adding a teardrop shape increases the tolerance for drill misregistration, thus improving the manufacturing yield and minimizing the chances of defects.
Teardrops become increasingly important as trace widths decrease. They are not usually needed for traces wider than 20 mils but are strongly recommended in flex PCBs, where they help resist cracking caused by vibration or bending forces.
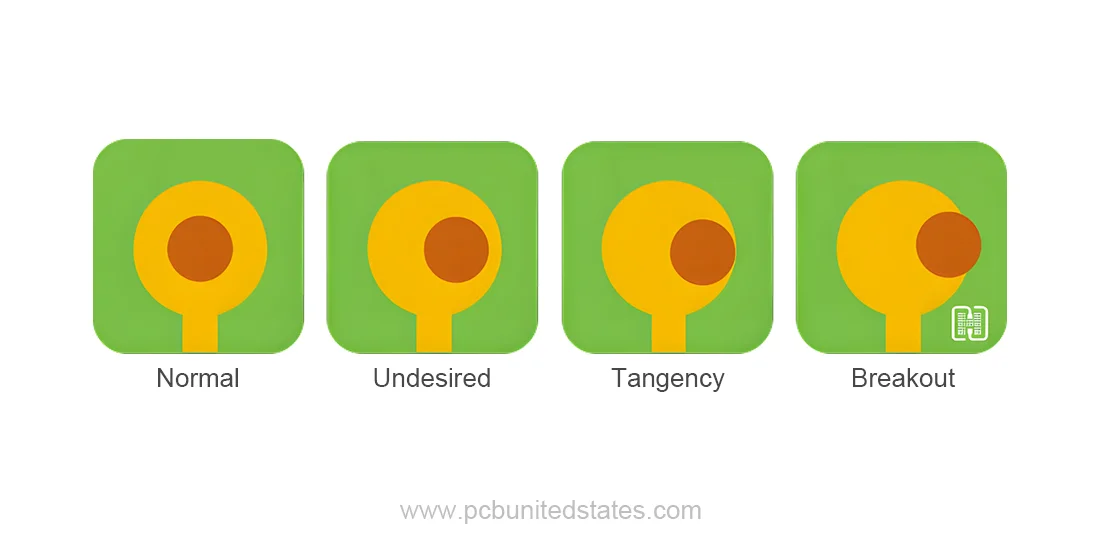
Common Annular Ring Problems and How to Avoid Them
If annular rings are not well designed and fabricated, several issues can occur that may affect the electrical performance of the board. The most common problems and how to avoid them are listed below:
Tangency
Tangency happens when the drilled hole hits the edge of the pad because of misalignment, or because the ring is too narrow for the hole size. This issue may lead to electrical disruptions and reliability issues. Tangency can be avoided by centering the holes and keeping the ring significantly wide.
Breakout
A breakout occurs when the drilled hole extends beyond the bounds of the annular ring and copper pad, breaking out of the pad area. This problem is usually caused by poor layer alignment in the PCB, with holes ending up in the wrong positions on different layers. In order to minimize the possibilities of breakout, annular ring should be designed in adequate width so that it could surround the hole properly.
Rupture
These rings are likely to develop cracks or fractures over time, which is known as rupture. A variety of reasons can cause this problem such as prolonged use, mechanical force or unfavorable environmental conditions. To avoid rupture, the use of durable materials and replacement of aging PCBs are effective methods.
Pad Lifting
This issue refers to detachment of the copper pad and annular ring from the PCB substrate. It can be caused by physical stress, thermal cycling, or poor bonding of materials. Preventive measures include using materials with high adhesion, minimizing heat exposure during production, and creating more effective pad design to better distribute mechanical stresses.
Essential Factors to Consider When Designing PCB Annular Rings
When designing PCB annular rings, several critical factors must be taken into account. These include the following:
- Width
Annular ring width is a key factor to consider during design, which should be wide enough to ensure stable electrical connection while conforming to the design limitations of the PCB. Adhering to industry standards such as IPC-2221 will help to ensure that minimum width requirements are met. What’s more, manufacturing tolerances should be considered during the design stage.
- Tolerances
During PCB fabrication, tolerances in drilling precision and hole drilling locations are unavoidable. Thus, when designing annular ring, these tolerances should be considered to ensure that even in cases of misalignment, there would still be sufficient copper to surround the hole to maintain connectivity. Most PCB manufacturers would provide the information regarding tolerances, which can be very useful when defining safe design margins.
- Pad-to-Hole Alignment
Perfect matching of the copper pad and the drilled hole is critical. Although the ring width is accurately designed, misregistration during the drilling operation may move the hole out of center so that the effective ring width is narrowed or even break the connection. To greatly minimize this risk, the designs should keep an adequate ring width to tolerate misalignment, and designers must ensure that the registration accuracy of their manufacturer adheres to the reliability requirements of their design.
Final Thoughts
Annular rings are fundamental to PCB reliability, serving as the critical connection between vias and board layers. Success lies in balancing competing requirements: rings must be wide enough for reliable connections yet compact enough to maximize board space, with sufficient tolerance margins for manufacturing variations.
Following industry standards like IPC-2221, understanding your manufacturer’s capabilities, and incorporating features like teardrops when needed.
If you need expert assistance with PCB design or manufacturing, feel free to contact us — our team is here to help ensure your designs are both reliable and production-ready.
Contact Us
Got any questions or inquiries? Fill out the form and we will get back to you soon

