What is the IPC2221 standard? The IPC-2221 standard serves as a foundational standard of PCB design since its first release in 1998. Establishing generic requirements for the design of organic PCBs, the standard is widely recognized in the electronic industry and used as an essential reference by PCB designers. Over years, the standard has undergone several major revisions. It has gradually improved principles and met more modern design needs, while also being supplemented by the IPC-2220 family. Understanding the standard comprehensively helps you design reliable and future-proof PCBs.
IPC2221 Standard and Its 3 Revisions
The IPC2221 standard has been updated 4 times by the Association of Connecting Electronics Industries (IPC), and each evolution comes along with important revisions and enhancements. The very first IPC2221 was released in 1998. It provides the baseline rules for PCB design, including layout principles, conductor spacing, trace width, pads and vias, material selection, and mechanical design. Meanwhile, it also established IPC-2220 as a series family that specializes in specific PCB designs. However, limited in simple technology and conservative data, IPC 2221 lacked the depth to address thermal, current-carrying capacity, and other modern issues, leading to the standard revision and revolution in later years.
IPC 2221A vs IPC 2221B vs IPC 2221C
IPC 2221A, the major version of the IPC 2221, was released in 2003. It added Appendix B, clarified a more comprehensive new standard of IPC 2152. It also clearly specifies the calculation method for clearance and creepage distance and adds some reliability-related parameters for design safety. Nevertheless, it still relies on an empirical formula, which is too conservative and has a distance from practice.
IPC 2221B is the second revised version released in 2012. This revision later became the foundational generic PCB design standard widely used for the long term. It incorporated feedback from IPC-2152 and corrected many outdated values for trace width and thermal rise. It also modernized rules and introduced the guidelines specific to emerging fields, like the Internet of Things (IoT).
IPC 2221B is complementary to IPC 2152 when it comes to conductor width, current-carrying capacity, and thermal management. The IPC 2152 with comprehensive testing provides the practical accuracy needed in modern PCB design, performing as the practical extension of IPC 2221B in the area of thermal design.
IPC 2221C is the latest version published in December 2023. The standard corrected earlier ambiguities, removed outdated guidance, and updated tables and design criteria. Importantly, IPC 2221C is fully modernized with high-frequency and high-speed design guidelines and advanced manufacturing techniques. IPC 2221C will become the go-to base reference for the modern PCB industry for a long time. However, it still needs to cross-reference other documents in the IPC 2152 and IPC 2220 series.
| Version | Major Revisions | Key Features | Limitations |
| IPC 2221 (1998) | First release, baseline standard for PCB design | Defined general requirements for PCB design | Lacked detailed thermal/current guidance; outdated with technological progress |
| IPC 2221A (2003) | Updated materials and design practices | Generic PCB design rules with improved guidance | Still relied on old current–temperature charts (less accurate) |
| IPC 2221B (2012) | Aligned with IPC-2152; Guidelines to the emerging fields | Clearer and expanded rules; Better linkage with IPC-2152 | More complex, still not covering high-speed designs fully |
| IPC 2221C (2023) | Modernized for HDI, high-speed, advanced materials | Integrates with new design standards; Fully aligned with IPC-2152 | Still evolving; Use with other documents |
Usage recommendation
IPC-2221 and IPC-2221A are considered outdated now and not recommended for new designs, but they are useful for you to understand the early PCB design standards.
IPC-2221B is still a safe baseline that can be used for general and simple PCB designs, but is limited for modern high-speed and high-frequency designs. You can combine IPC 2152 for accuracy and reliability when it comes to thermal and current design.
IPC-2221C is the default choice for modern electronic design needs, especially high-density, high-speed, or reliability-critical designs like 5G telecom and medical devices.i It aligns with IPC-2152 with modern stack-up practices and improved reliability testing, recommending for future products expected to last for years.
Key Functions of IPC2221 in PCB Design
IPC2221 functions as a universal rulebook for PCB design. It provides general guidance on material, conductors, holes and vias, thermal control, mechanical structure, electrical performance, and many other aspects. Let’s have a look at one by one.
Conductor design
IPC-2221 provides rules for IPC designers to determine conductor width, spacing, and thickness to ensure reliable current capacity to avoid overheating. It introduced formulas and charts for trace width calculation based on temperature rise, current, and copper thickness, balancing electrical performance and reliability.
Material Selection
The standard defines guidance on choosing laminate and prepreg material. It emphasizes the practical needs to match material to the end-use environment and provide guidance based on properties such as thermal expansion, dielectric constant, and mechanical strength to ensure reliability.
Plated-Through Holes and Vias
IPC2221 clarifies the rules for hole sizes, annular rings, aspect ratios, plating thickness, and recommendations for via types and their structural integrity in multilayer boards. This ensures reliable electrical connections between layers and avoids thermal cycles and mechanical stress.
Thermal Management
The standard guides how to manage heat dissipation on the PCB. It includes the use of thermal relief, heat spreading planes, and copper pour to maintain a stable status and operation. IPC-2221 also guides board design and the placement of components to avoid hotspots, protecting the board substrate and components from thermal stress.
Mechanical Design & Reliability
IPC-2221 offers rules for board outline, panelization, mounting hole placement, withstanding handling, assembly, vibration, and other mechanical forces. The document guides overall mechanical robustness for the PCB to maintain reliability.
Electrical Performance Requirements
The standard offers guidance on controlled impedance, crosstalk, signal integrity, and dielectric spacing, helping maintain electrical reliability, reduce electromagnetic interference, and comply with the performance of various applications.
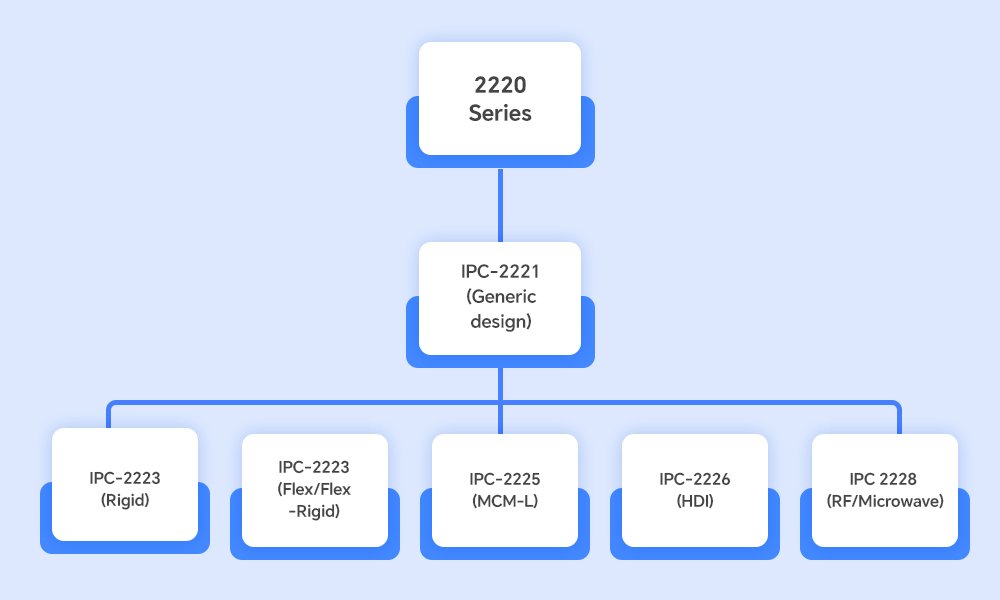
IPC 2220 Series Hierarchy: The Essential Supplement to IPC2221
IPC 2220 series supplements IPC 2221 with standards for specific PCB designs, like rigid, flexible, and rigid-flex PCB designs. In this family of standards, IPC2221 is the generic and overarching standard for PCB design, and other standards in the series focus on other specific applications.
IPC-2221—generic standard on PCB design
IPC-2221 is the foundation document for all printed circuit board designs. It provides general guidance, like trace width, spacing, and material, for each type of PCB. All other sub-standards in the IPC2220 family are built on this base.
IPC-2222 for Rigid organic printed board design
IPC-2222 mainly focuses on the design of rigid PCBs that are made from organic materials like FR4. It provides guidance on conductor width, layer stack-up, manufacturability, and via structures. It is widely used for consumer electronics, industrial control boards, and other applications with rigid boards.
IPC-2223 for Flexible and rigid/flexible printed board design
IPC-2223 provides guidance for flexible and rigid-flex PCBs. It deals with bend radius, dynamic flexing, material choices, and mechanical design to ensure reliability under repeated vending and thermal cycling. It plays an important role in applications that require great flexibility and compactness, such as medical devices, wearable electronics, and aerospace systems.
IPC-2225 for Organic, MCM-L, printed board design
IPC-2225 is applied to organic substrate-based multichip modules, which integrate multiple bare chips together on one board. It guides in high-density interconnections, signal integrity, reliability, and other design rules for these modules, typically used for advanced computing and telecommunications.
IPC-2226 for High-Density Interconnect (HDI) printed board design
This standard is specifically used for HDI PCBs. It defines rules for via-in-pad structures, sequential build-up, thin dielectric layers, and so on. It is fundamental for mobile devices, high-speed networking, and many other compact and performance-demanding applications.
IPC-2228 for RF/Microwave printed board design
IPC-2228 is tailored for modern RF and microwave PCBs. It is responsible for controlled impedance, low-loss materials, transmission line design, and other factors that are important for high frequencies. It is especially essential for applications like wireless communication, radar, satellite, and many other high-frequency applications
Note: IPC 2224 was canceled by the IPC, and the relevant PCB forms had been transferred to the revision of IPC-2221 and IPC-2222 since 2012, when IPC2221B was released. IPC-2227 was not developed and released.
Conclusion
The IPC2221 has proven its importance in overall PCB designs through years of revolution. From early baseline rules to the latest modern IPC-2221C guidance, the standard provides PCB designers a reliable framework to follow. What’s more, the supplementary IPC-2220 series also supports IPC2221 in some specific PCB designs. It is important for anyone who engages in PCB design and manufacturing to stay informed about the latest standards and principles in the industry to help designers achieve reliable and high-quality PCBs. If you have doubts about your PCB design or need a trusted manufacturer, try to contact MOKOPCB! Our expert can provide you with optimal solutions to fully meet your project requirements.

