PCB surface finish is not just for protection, it can also affect the soldering process and impact board performance. It’s tricky to choose the right finish for your board, considering numerous factors. HASL vs ENIG are considered two popular options. When choosing between them, many engineers usually get into a struggle. This is because HASL and ENIG differ significantly in many aspects and have distinct advantages and disadvantages. In this blog, we will reveal the top 8 differences to help you clear all the confusion and choose the right finish.
A Quick Overview of HASL and ENIG
HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling): HASL is famous for its cost-effectiveness. The PCB is first dipped in molten solder, and then it is leveled using hot air. To get rid of extra solder, a hot air knife is blown across the PCB surface.
ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold): ENIG is a more reliable and sophisticated technique. It requires depositing a nickel layer on the copper pads and traces first, followed by a thin gold layer.
HASL vs ENIG: What Are the Key Differences?
1. Process Differences Between HASL and ENIG
- Hot Air Solder Leveling Process:
Step 1: Cleaning
Use mechanical or chemical methods to clean the board, removing debris, dust, or other contaminants.
Step 2: Applying Flux
Apply the PCB flux to the board, avoiding oxidation and increasing the solder wetting.
Step 3: Preheating
It’s important to preheat the PCB up to 150℃ to avoid thermal shock.
Step 4: Solder Immersion
Immersed the board in the molten solder bath, where the temperature commonly is up to 230-260°C. With a lead-free process, it needs to reach 250-280°C.
Step 5: Hot Air Levelling
Excess solder can be removed with the hot air. The temperature can go up to around 400-450°C.
Step 6: Cooling Process
In order to solidify the solder, cool down the PCB to ambient temperature.
Step 7: Post-Cleaning
Clean the board to remove any excess flux.
- Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold Process:
Step 1: Cleaning
Same as HASL, to completely clean the PCB, avoiding any contaminants on it.
Step 2: Nickel Deposition
The electroless plating process deposits a 3 to 6μm nickel layer on pads and exposed traces, preventing gold from diffusing into the copper.
Step 3: First Rinsing
Rinse the PCB to remove the nickel solution.
Step 4: Gold Deposition
The board is immersed in a gold solution, depositing a thin gold layer of 0.05 to 0.1μm thick on the surface of nickel.
Step 5: Final Rinsing and Drying
Finally, rinse the excess gold solution from the circuit board. Then, clean and dry it.
2. Surface Flatness Differences in ENIG vs HASL
HASL usually produces a thick and uneven surface, limiting its use for fine-pitch components (<0.5 mm). Its surface deviation reaches 10-20 µm. ENIG can provide a very flat surface, which is critical for high-density PCB designs. The surface deviations are usually less than 0.1 µm.
3. Cost Difference
HASL is a cost-effective PCB finish and is a frequent choice for numerous uses. ENIG may cost more, as this technique is more complex and the gold material needs to be used. However, it is preferred for designs that require superior performance and long-term durability.
4. Comparing the Reliability of ENIG and HASL
ENIG has a thin nickel layer topped with an immersion gold layer, which is harder, more corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant. The nickel layer prevents the gold from moving into the copper substrate by acting as a barrier. This can maintain strong adhesion over time, avoiding soldering problems. Furthermore, the gold layer has excellent solderability and conductivity, which is critical for HF applications and fine-pitched components.
In contrast, HASL with tin-lead coating is softer. It’s more susceptible to growing whiskers, which may lead to electrical shorts and other problems.
5. Lifespan Comparison Between HASL vs ENIG
ENIG has a longer life cycle, making it the first choice for medical, aerospace, and automotive applications. It has a 12- to 18-month shelf life. HASL has a relatively shorter lifespan, which can be chosen for general-purpose or cost-sensitive applications. Its shelf life is usually between 6 and 12 months.
6. Solderability & Corrosion Resistance
ENIG offers a smooth and shiny gold layer, which has excellent solderability. The gold layer also provides additional protection to prevent oxidation and ensure long-term operation. Nickel protects against damage from chemicals, making it last longer.
HASL can also have good solderability, but this is not enough for small or fine-pitch components. Its rough surface is adequate for THT components. In contrast to ENIG, it has a lower level of corrosion resistance. HASL surfaces can oxidize or tarnish, especially in humid and harsh environments.
7. HASL vs ENIG Have Different Variants
HASL Variants
- Leaded HASL – Commonly used solder alloys containing tin (63%) and lead (37%).
- Lead-Free HASL – Uses lead-free solder alloys, typically tin with small amounts of copper or silver, to replace lead.
ENIG Variants
- ENEPIG (Electroless Nickel Electroless Palladium Immersion Gold) – Between the gold and nickel, a thin layer of palladium is deposited to stop the nickel from corroding.
- Hard Gold ENIG – Add a thick gold layer on the nickel. The hardness of hard gold ENIG ranges from 130–200 HK25.
- Soft Gold ENIG – Uses a thinner and softer gold layer with a hardness of around 20–90 HK25.
8. ENIG vs HASL: Environmental Considerations
Nowadays, the environmental impact of PCB manufacturing is receiving increasing attention. The traditional HASL contains lead in the tin-lead coating, which brings a higher environmental impact. This makes HASL less sustainable, especially for applications with strict environmental requirements.
However, lead-free HASL and ENIG are compliant with RoHS compliance, not using the harmful lead. Thus, ENIG is generally considered a more environmentally friendly option, producing fewer hazardous byproducts during manufacturing and disposal.
HASL vs ENIG: Quick Comparison Table
| Aspect | HASL | ENIG |
| Cost | Low, economical for budget-limited projects | High, ideal for critical and high-reliability uses |
| Composition | Tin-lead or lead-free solder | Nickel and gold |
| Surface Flatness | Relatively thick and uneven | Excellent flatness |
| Thickness Uniformity | Inconsistent | Uniform |
| Component Compatibility | Less suitable for fine pitch SMT components | Ideal for fine pitch components |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Solderability | Good | Excellent |
| Lead-Free Compatibility | Good, lead-free options available | Excellent |
| Suitability for Harsh Environments | Not recommended for harsh environments | High tolerance to harsh conditions |
| Shelf-Life | Shorter, prone to oxidation | Longer, gold layer resists oxidation |
| Repairability | Easy to rework thanks to solder’s properties | Hard nickel surface makes rework difficult |
| Best for | General electronics, consumer devices | Aerospace, medical and high-performance uses |
HASL and ENIG: What Are the Pros and Cons?
After learning the 8 key differences between HASL vs ENIG, you should now have a deeper understanding of each option. Next, let’s take a look at the following pros and cons to help you decide which surface finish best fits your PCB requirements.
Pros of Hot Air Solder Leveling
- Budget-FriendlyOption: It’s one of the most cost-effective finish choices, which is suitable for mass production or budget-sensitive projects.
- Easy Rework:Hot air solder leveling coatings are primarily solder, making them particularly convenient for rework.
- Soldering Versatility:HASL is compatible with different soldering methods, like reflow soldering, wave soldering, hand soldering, etc.
Cons of Hot Air Solder Leveling
- Uneven surface:The HASL coating is relatively thick and uneven, potentially making soldering fine-pitch SMT components or high-density boards more difficult.
- Environmental Concerns:Lead HASL is not compliant with the RoHS standard, while lead-free alternative ones need to cost more.
- Susceptible to Oxidation:Over time, the tin-lead surface might be vulnerable to oxidation. Thus, it can highly affect solderability if the boards are stored for a long time.
Pros of Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold
- Surface Flatness:ENIG has a superior flat surface. The thin gold layer offers an ultra-flat surface to establish a dependable connection, which is critical for BGA packages or fine-pitch components.
- Excellent solderability:The gold layer is greatly solderable, which can form strong and reliable solder joints. With even surface and consistent thickness, it’s easier to form a robust connection.
- Corrosion Resistance:The PCB’s shelf life and dependability are increased by ENIG’s top gold layer, which shields the copper and nickel underneath from oxidation and corrosion.
Cons of Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold
- Higher Cost:With expensive materials (gold and nickel) and a complex process, it’s obvious that this finish costs more than HASL.
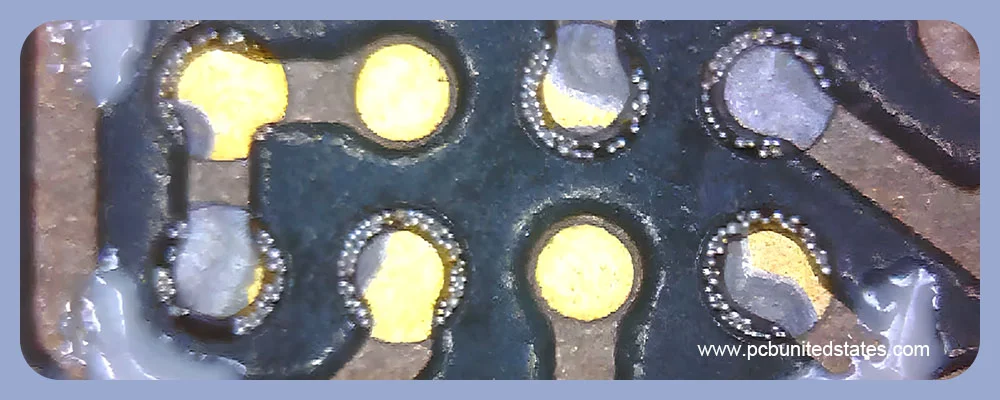

- Black Pad Defect: It occurs when the nickel layer is improperly plated or corrodes, causing poor solder joints or other issues. The affected nickel surface can appear black. That’s why this phenomenon is called Black Pad.
- Hard to Rework: The hard nickel layer beneath the gold is prone to corroding under high temperatures. Therefore, it’s challenging to control the temperature during the repair step, making rework slower and more costly compared to HASL.
HASL vs ENIG: How to Decide the Right PCB Finish
When choosing between HASL vs ENIG, you should take into account some critical factors to balance the cost, performance, manufacturing, etc. To assist you in making the best decision, the table below shows the scenarios where each finish performs best.
| Scenario | HASL | ENIG |
| General consumer electronics (household appliances) | ✅ | ❌ |
| Highly reliable uses (aerospace or medical devices) | ❌ | ✅ |
| High-density boards / fine-pitch components | ❌ | ✅ |
| Harsh environments (high humidity, corrosion-prone) | ❌ | ✅ |
| RoHS Compliance | ✅(Lead-free HASL) | ✅ |
| Cost-sensitive projects | ✅ | ❌ |
| High-frequency/high-speed signals | ❌ | ✅ |
| Extended Shelf Life | ❌ | ✅ |
| Fast Production | ✅ | ❌ |
Key Takeaways:
- For high-volume, cost-driven projects where a speedy turnaround is essential, HASL is perfect.
- ENIG provides superior reliability and is preferred for high-density, high-frequency, or harsh-environment applications.
Wrap Up
To sum up, HASL vs ENIG are two commonly used PCB finishes, each suited for different applications and requirements. When choosing between them, it’s necessary to consider many critical factors. As a professional PCB & PCBA manufacturer, we can provide one-stop services, including different PCB surface finish options. No matter ENIG, HASL, or other finishes, we can give you an expert solution. Contact us to start the next project!

