In practical applications, various environmental factors (such as moisture, dust, and chemical exposure) can affect PCB performance, ultimately impacting the durability and reliability of electronic devices. Therefore, it’s critical to protect circuit boards from environmental influences effectively. PCB potting vs. conformal coating are two primary circuit board protection methods. However, which one is appropriate for your PCB? Read this blog to find out.
PCB Potting vs. Conformal Coating: A Quick Overview
What Is PCB Potting?
PCB potting involves completely encapsulating a PCB in a protective material to protect it from environmental influences such as moisture, chemicals, and vibration. This protective material is typically a liquid or gel-like substance, also known as a PCB potting compound. Once the material cures, the circuit board and components are permanently encapsulated.
What Is Conformal Coating?
A PCB can be shielded from low-level environmental elements like moisture, dust, and corrosion by applying a thin polymer film called conformal coating. It can significantly increase the lifespan and reliability of the board while still allowing for later inspection or repair.
Key Differences Between Potting and Conformal Coating
After learning the overview of PCB potting vs. conformal coating, we list their key differences to help you gain a deeper understanding and choose the right one.
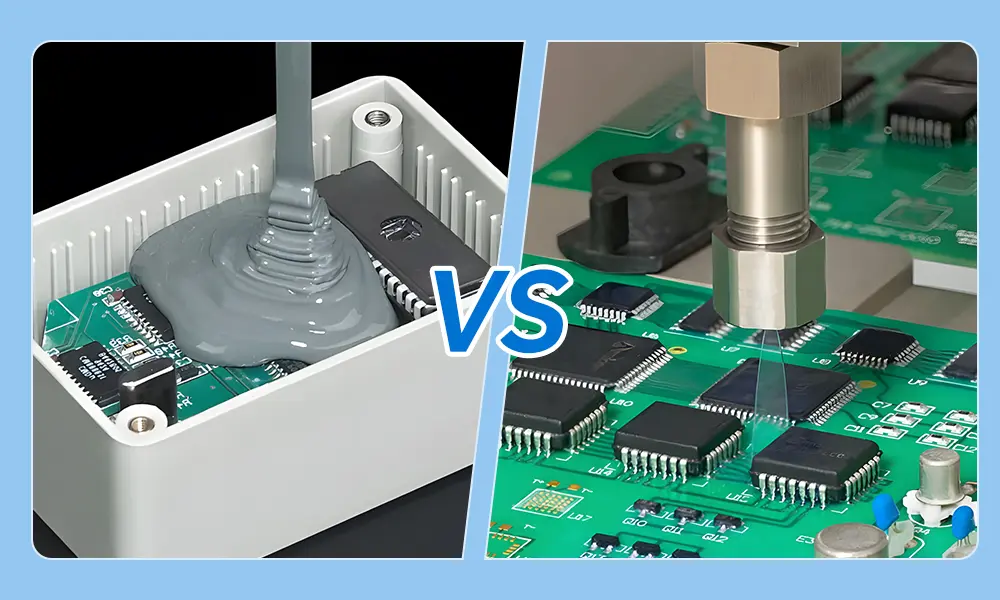
Coverage and Protection Level
PCB potting creates a sealed and permanent barrier to protect the PCB, offering an excellent protection level. While conformal coating only forms a barrier on the PCB surface, it ensures the circuit board is protected against dust, moisture, and chemicals from the standard environment.
Flexibility and Rework
When the potting materials cure, it is challenging to access, test, or repair the components. If you need to repair or replace the components, the circuit board potting compounds need to be removed. It’s a time-consuming process. However, PCB coatings are easily removed and reapply. If rework or repair is needed, you can remove the small part of the coating. Meanwhile, you can easily access the components for testing when the coating is applied.
Chemical Resistance
PCB potting vs. conformal coating have different chemical resistance. Potting materials can withstand many types of chemicals and corrosive substances. It is ideal for devices exposed to harsh and extreme chemical conditions. For conformal coating, it has a limited ability to protect against oils, solvents, and some chemicals. Its chemical resistance also depends on different coating materials.
Application Method
PCB potting vs. conformal coating differ in application complexity. PCB potting is more complex, encapsulating the whole PCB. It involves using special equipment and materials. Conformal coating is easier to apply to the PCB surface, using brushing, dipping, spraying, or selective coating.
Cost
Unlike conformal coating, PCB potting materials and equipment are relatively expensive, increasing the total cost. However, PCB coating materials are cost-effective, and the application methods are simple, reducing the overall cost.
| Aspects | PCB Potting | Conformal Coating |
| Coverage | Completely and permanently potting the entire PCB | Apply a thin protective layer over the PCB surface |
| Protection Level | High | Moderate |
| Material Used | Epoxy resins, Acrylic resin, Polyamide, Silicone rubber | Acrylic, Parylene, Epoxy, Urethane, Silicone |
| Material Thickness | Thick, usually 1 to 10 millimeters | Thin, typically 25 to 250 micrometers |
| Application Method | Poured the potting compound into molds or enclosures | Brushing, dipping, spraying, or selective coating |
| Flexibility and Rework | Less flexible, hard to inspect, repair, and rework | High flexibility and easy to inspect, repair, and rework |
| Vibration & Impact Resistance | High, provides excellent mechanical support and absorbs shocks effectively | Low to moderate, the thin PCB coating offers limited mechanical protection |
| Cost | Higher material and processing costs | Lower material cost and simpler process |
| Weight and Size Impact | Adds significant weight and bulk | Minimal impact on weight and dimensions |
| Typical Use Cases | Extreme and hash environment, high vibration applications or components requiring sealing | General environment, moisture and dust proof, or requiring subsequent repair |
Pros and Cons of Using Circuit Board Potting and Conformal Coating
The purpose of PCB potting vs. conformal coating is the same: protecting the circuit board. Every approach has benefits and drawbacks. As long as they are selected and used in appropriate application scenarios, both can be effective.
PCB Potting: Pros and Cons
PCB potting is a popular circuit board protection method, easily applied in mass production and assembly lines. It offers other benefits:
– Better heat resistance, chemical resistance, vibration resistance, and shock resistance
– Reduce the risk of reverse engineering when using dark-tinted potting compounds
– Effective barrier against humidity and electrical arcs
– Higher durability than conformal coating, especially in extreme conditions
However, it also has some drawbacks:
– Challenge to repair or rework the PCBA
– Increase weight and size, which may impact the PCB design
– A complex application process
– Increased cost, less cost-effective than conformal coating
Conformal Coating: Pros and Cons
Compared with PCB board potting, conformal coating is very thin, minimizing the increase in weight. The following are some benefits of PCB conformal coating:
– Thin coating layer, ideal for tight tolerances
– Effective protection against problems such as dust, moisture, salt spray, and corrosion
– A cost-effective option, costs less than circuit board potting
– High flexibility, easy to rework and repair
The downside of conformal coating is its limited protective capabilities, especially in extreme environments. Here are the drawbacks, including:
– Does not have the same durability as potting.
– Does not provide full protection like PCB potting
PCB Potting vs. Conformal Coating: When to Use Each for PCB Protection
Knowing the pros and cons of PCB potting vs. conformal coating, you may better decide which fits your project’s needs. Here are some practical guidelines to help you choose the right protection solution.
When to Use PCB Potting?
For harsh and extreme conditions – If your PCB is exposed to corrosive chemicals, extreme temperatures, or heavy vibrations, PCB potting offers superior protection.
Full encapsulated requirement – When the PCB needs to be sealed completely, potting is a prior option. It’s ideal for water immersion or dust-heavy environments.
Enhanced mechanical strength – Once the PCB has to withstand heavy physical shock and vibration, circuit board potting can provide better mechanical support.
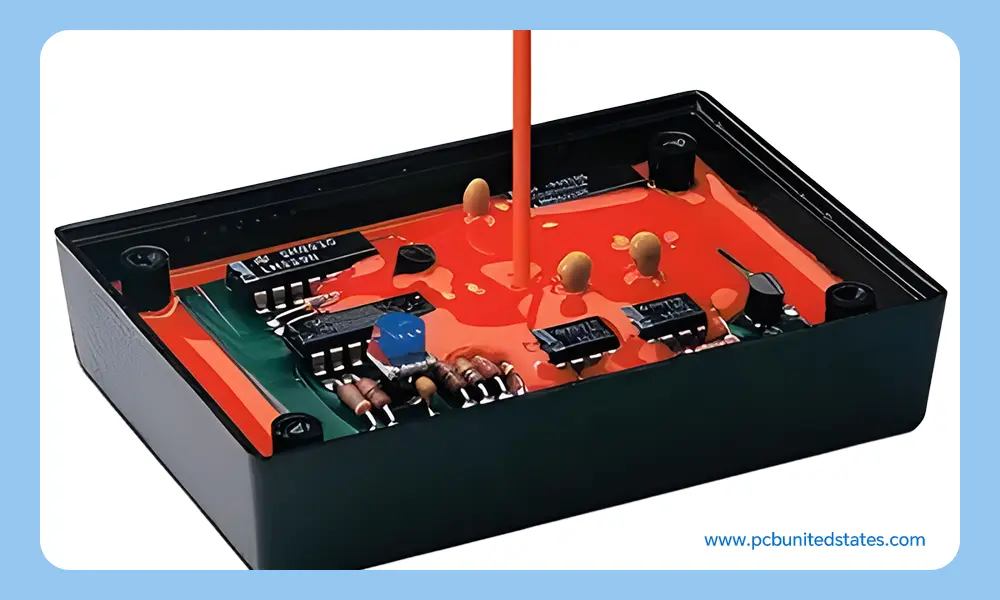

Secure sensitive and privacy design – When using dark-colored or opaque materials, it’s easy to protect your PCB design, avoiding tampering or reverse engineering.
When to Use Conformal Coating?
For standard environment – In standard environment conditions, the PCB mainly requires protection against moisture, dust, etc.
Easy maintenance and rework – Coatings can be removed easily to conduct later maintenance and repair.
Space-constrained applications – Conformal coating is a thin layer applied to the circuit board surface, which is beneficial for compact or lightweight devices, such as handheld electronics and smartphones.
High-volume, cost-sensitive production – The PCB coating can be applied quickly and economically in large-scale production.
Contact MOKOPCB Today for Circuit Board Protection
Neither method is superior nor inferior. The key lies in whether it meets the protective performance requirements of the specific application. When choosing between PCB potting vs. conformal coating, you should consider many factors such as the equipment’s intended use, the actual operating environment, and cost. Our knowledgeable experts can help if you’re still not sure which approach is best for your PCBA. With extensive experience, MOKOPCB will collaborate closely with you to offer a tailored solution.
FAQs About PCB Potting vs. Conformal Coating
- What are the different kinds of conformal coatings?
These are 5 frequently used coating materials: acrylic resin, epoxy resin, polyurethane resin, silicone, parylene, etc. Each offers different properties and protection levels.
- How to apply conformal coating to a circuit board?
It is easy to apply conformal coating to the PCB surface, including spraying, brushing, dipping, and selective coating. The choice depends on production volume, coating materials, and design complexity.
- What are the commonly used PCB board potting materials?
These are commonly used PCB potting compounds: epoxy resins, acrylic resin, polyamide, silicone rubber, etc. Each material has different properties in chemical resistance, thermal performance, and mechanical strength.
- How to select the suitable PCB potting compounds?
When choosing potting compounds for PCB, you have to consider these key factors: hardness, thermal conductivity, viscosity, and color.

