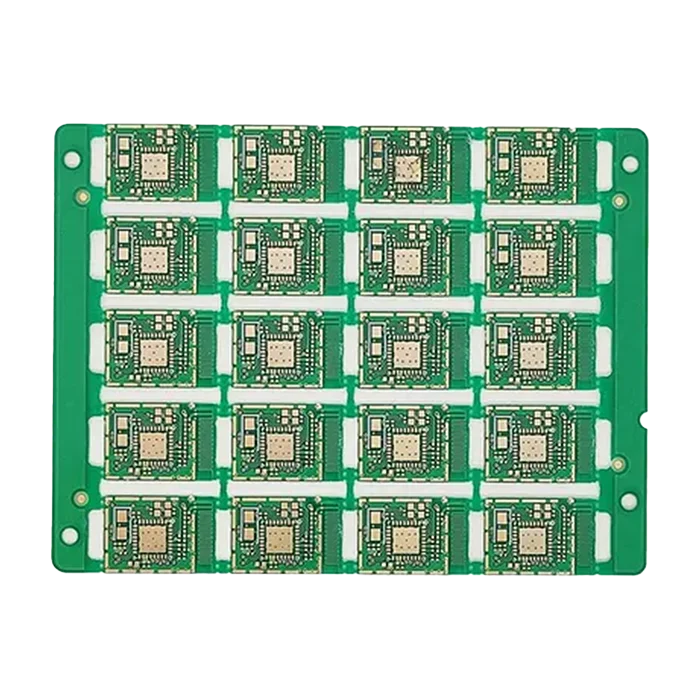
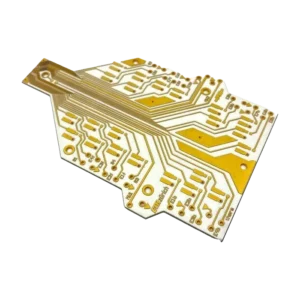
2-16 layer HDI multi-layer PCB
$75.90
2 to 16 layers of HDI multi-layer PCB have a corresponding number of conductive layers. HDI (High Density Interconnect) circuit boards have a compact design with smaller vias, pads, and traces, allowing the same functions as standard circuit boards, but in a smaller size. They have high-density interconnection capabilities, supporting the miniaturization of electronic products.
Shipping fee and delivery date to be negotiated. Send inquiry for more details.
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Claim a refund if your order is missing or arrives with product issues, our support team would deal with your refund within 24 hours.
| Layer Counts | 16L |
| Base Material | FR-4 |
| Board Thickness(mm) | 1.6 |
| Max board size(mm) | 570*670 |
| PCB size tolerance | ±0.3mm |
| Min. Hole Size | 0.15mm |
| Min. Line Width | 5mil |
| Copper Weight | 2oz |
| Surface Finish | ENIG |
| Certificate | UL, RoHS, ISO, and REACH |
 2-16 layer HDI multi-layer PCB
2-16 layer HDI multi-layer PCB
| 5 star | 0% | |
| 4 star | 0% | |
| 3 star | 0% | |
| 2 star | 0% | |
| 1 star | 0% |
Sorry, no reviews match your current selections
Questions & Answers
1.What payment options do you offer?
We accept different payment methods like T/T, West Union, Money Gram, L/C, and PayPal (for sample orders). Please get in touch with our sales representatives for more details.
2.What are the quality standards MOKOPCB adheres to?
At MOKOPCB we strictly adhere to IPC-A-600 for printed circuit boards and IPC-A-610 for assembled boards to ensure top quality.
3.What is the difference between HDI and standard multilayer PCBs?
HDI PCBs use ultra-thin traces and laser-drilled microvias to achieve high-density interconnects. Standard multi-layer PCBs typically use mechanically drilled through-holes and wider traces, and their designs are relatively simple.
4.What design considerations are important for 2-16 layer HDI multilayer PCBs?
When designing an HDI multilayer PCB, it’s essential to consider factors like impedance control, thermal management, EMI, EMC, space constraints, and sequential buildup.